Birds aren’t robots, but their brains are flash drives
With apologies for contradicting the weird stickers and meme-obsessed teenagers you’ve been seeing for the last few years, birds are actually quite real. They aren’t robots built by the government to spy on you. But, at the risk of contradicting myself, their brains are computers. Let me explain—or rather, let me sum up since there is too much.
You probably know that birds are smarter than we give them credit for. Corvids like crows and ravens can be as smart as human children, with a shocking capacity to retain information. YouTuber and audio scientist Benn Jordan knows this, and he knows that the sounds birds make to communicate between themselves can be incredibly complex. But is it complex enough to retain and transmit digital information? The digital information of an image made and encoded by humans, perhaps?
Turns out, yes! Over a few months, Jordan studied several species of birds to find complex birdsong, settling on the European starling for its intelligence and impressive ability to mimic sounds with the specific structure of its lungs and larynx. Specifically, he visited The Mouth, a semi-domesticated rescued starling owned by Sarah Tidwell, who has been around humans his whole life.
Almost as a goof, Jordan drew a simple photo of a bird in a spectral synthesizer. (This is an extremely basic way of representing audible sounds as a 2D image.) Jordan then played the sounds corresponding to the image to The Mouth (the starling). While Jordan didn’t immediately hear the bird repeat the sequence of sounds corresponding to the image during his visit to Tidwell’s home, after analyzing the recordings of his visit, he spotted something strange in the visual graph of the recordings.
Benn Jordan’s original image and The Mouth’s audio recreation, visualized. Benn Jordan
There was the bird drawing. The one that Jordan had drawn in the synthesizer days or weeks previously, reproduced in the starling’s song, and showing up in a completely different visualization of the data. While the reproduction isn’t digitally perfect, Jordan estimates that The Mouth effectively retained and re-transmitted 176 kilobytes of data in audio format. Not enough to replace your SSD, perhaps, but more than enough to transmit, say, a large text file. Oh crap, maybe the birds are spying on us after all.
Bird mimicry isn’t anything new, of course. And again, we’ve known for a while that birds can be much more intelligent than we previously assumed, especially when you expand the definition of “intelligence” beyond a human standard. But the ability of The Mouth to so accurately retain and then transmit data is incredible, and Jordan’s video is such a vivid, literal illustration of that ability. 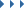
© 2025 PC World 2:55am  
|
|
|
 |
|